Dear customers and friends:
Introduction
In the realm of precision engineering and industrial manufacturing, the choice of fasteners can significantly impact performance, safety, and longevity. Chrome Button Head Screws represent a cutting-edge solution designed to meet the demands of high-stakes industries. These screws combine advanced material science, precise engineering, and rigorous quality standards to deliver unmatched reliability. This article delves into the product features, technical specifications, and applications, while also highlighting the company behind this innovation.
Product Overview
Chrome Button Head Screws are engineered to address the challenges of modern engineering. Their design prioritizes load distribution, torque efficiency, and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for applications where performance and durability are non-negotiable. The product is manufactured by Shijiazhuang Dellee Ming Garments Co., Ltd., a company with over two decades of expertise in fastener solutions and global export operations.
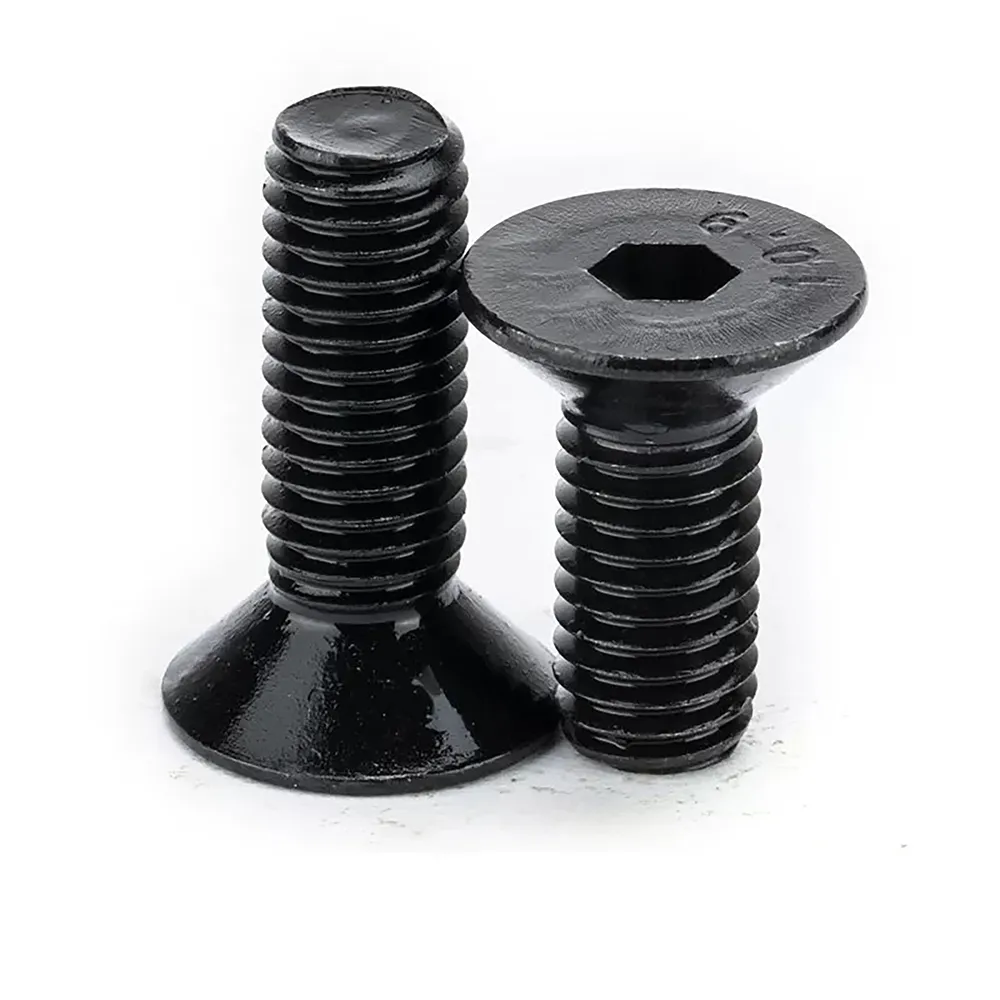

Key Features and Technical Advantages
Optimized Load Distribution
One of the standout features of Chrome Button Head Screws is their radially curved bearing surface, which minimizes point loading on soft substrates such as composites and cast alloys. This design reduces the risk of material deformation and ensures even stress distribution, enhancing the structural integrity of the assembled components. For instance, the head height tolerance is tightly controlled at ±0.20mm, significantly tighter than the DIN 912 standard (e.g., M6: 4.0mm vs. DIN 912’s 6.0mm). This precision is critical in aerospace and automotive applications where weight savings and material preservation are paramount.
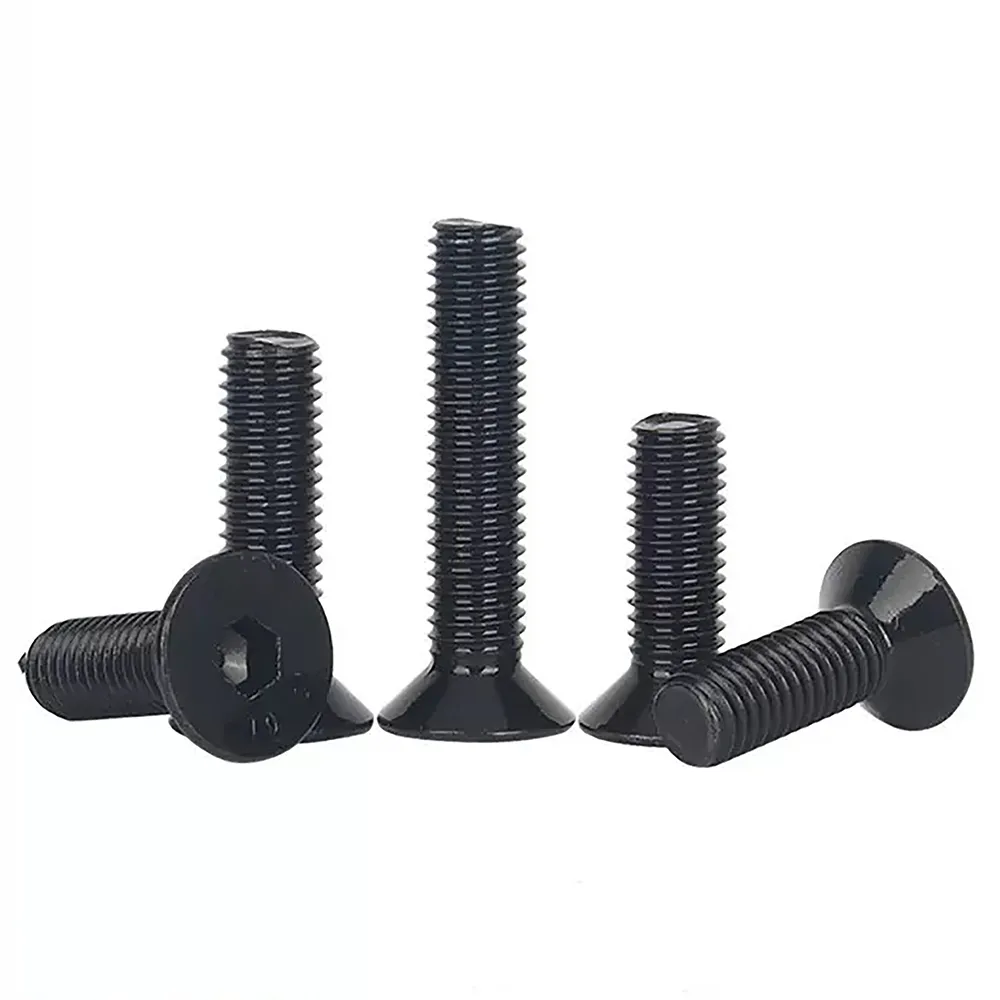

High-Torque Drive System
The extended socket depth of these screws meets the stringent requirements of DIN 7991:2014 Section 4.3, with a depth of at least 1.5× the nominal diameter. This design ensures secure engagement with tools, reducing the risk of stripping during installation. Additionally, the drive conformity adheres to ISO 10664 Class C standards, with a tolerance of ±0.028mm. This level of precision guarantees consistent performance, even under high-torque conditions, making these screws suitable for demanding environments like industrial machinery and heavy-duty equipment.
Performance-Graded Materials
Chrome Button Head Screws are crafted from SCM435 alloy steel, offering multiple strength classes: 12.9, 10.9, and 8.8. These grades ensure the screws can withstand extreme mechanical stresses. For corrosion resistance, the screws undergo black oxide treatment (≥96 hours of salt spray resistance) or Geomet® coating (≥720 hours of corrosion protection). Such treatments are essential in industries like marine engineering and medical devices, where exposure to harsh environments is common.

Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Material | SCM435 Alloy Steel |
| Strength Classes | 12.9, 10.9, 8.8 |
| Corrosion Protection | Black Oxide (≥96h salt spray), Geomet® Coating (≥720h) |
| Head Height Tolerance | ±0.20mm |
| Socket Depth | ≥1.5× Nominal Diameter (DIN 7991:2014) |
| Drive Conformity | ISO 10664 Class C (±0.028mm) |
| Head-to-Shank Transition Radius | ≥0.1d (vs. DIN’s ≥0.08d) |
Applications in Critical Industries
Chrome Button Head Screws are engineered to excel in specialized environments. Here are some key applications:
Aerospace
In aerospace, weight reduction is critical. The reduced head height of these screws allows for lighter turbine assemblies without compromising structural integrity. This feature aligns with NIST’s research on material efficiency and lightweight design, which emphasizes minimizing material use while maintaining performance (NIST, 2023).
Automotive
The radially curved bearing surface prevents thread galling in aluminum engine blocks, a common issue in automotive manufacturing. This design reduces maintenance costs and enhances vehicle reliability. According to NIST’s standards for mechanical systems, such innovations are vital for improving the durability of automotive components (NIST, 2022).
Medical
For medical devices, passivated stainless steel ensures biocompatibility, meeting ISO 13485 standards. This makes the screws suitable for implants and surgical instruments, where contamination and corrosion are unacceptable risks.
Precision Engineering
The head-to-shank transition radius of ≥0.1d reduces stress concentration, preventing fatigue failures in precision machinery. This design is particularly beneficial in CNC equipment and robotics, where high-cycle accuracy is required.

Company Background and Commitment
Shijiazhuang Dellee Ming Garments Co., Ltd. has established itself as a leader in the fastener industry, with over 20 years of experience in global exports. The company’s expertise in international logistics and compliance ensures seamless delivery of products to clients worldwide. Their commitment to quality is reflected in the certified export documentation and custom packaging with pre-shipment visual verification, providing customers with peace of mind.
Additionally, the company offers instant quote responses and customizable spec sheets, empowering buyers to make informed decisions. Their after-sales support guarantees swift resolution of technical issues, reinforcing their reputation for reliability and customer-centric service.
Conclusion
Chrome Button Head Screws exemplify the convergence of advanced engineering and material science. With their optimized load distribution, high-torque drive systems, and corrosion-resistant properties, these screws are indispensable in aerospace, automotive, medical, and precision engineering applications. Backed by Shijiazhuang Dellee Ming Garments Co., Ltd.’s 20+ years of global expertise, the product offers a blend of performance, reliability, and value. For industries demanding excellence, these screws are a testament to innovation and quality.
References
NIST. (2023). Material Efficiency and Lightweight Design. Retrieved from https://www.nist.gov
NIST. (2022). Standards for Mechanical Systems. Retrieved from https://www.nist.gov
Post time: Aug . 14, 2025 12:15